No products in the basket.
HAKKO, Product catalogue, Shape BC/C, Shop by brand, Soldering iron tips, T15 series
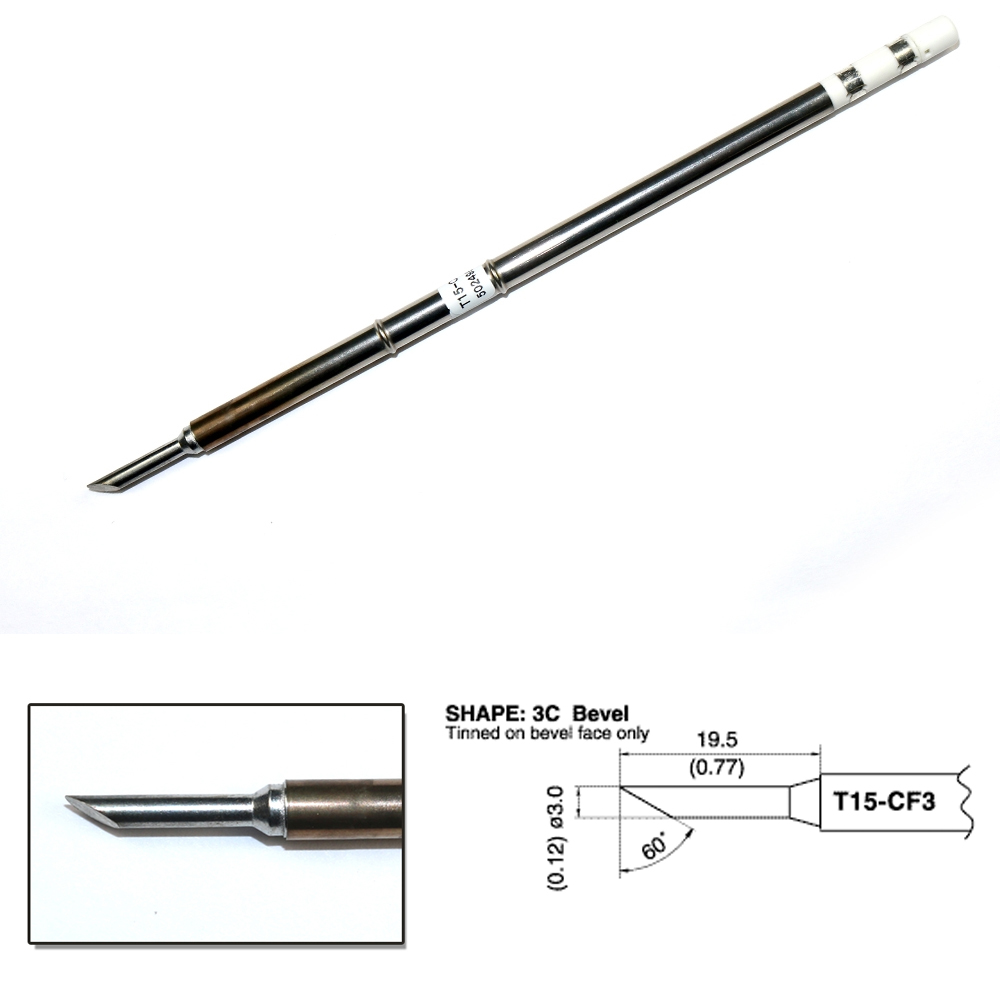
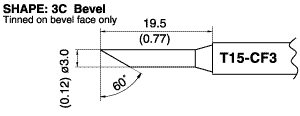
T15-CF3 Bevel Soldering Tip 3mm/60°x 19.5mm
SKU: HT15-CF3
Availability:
In stock
T15 Series Tip For use with the FM2027 / FM2028 Soldering Irons
£45.55 Excl. VAT
In stock
How to use Shape BC/C and examples
This type has a shape like a cone or column cut at a slant, which allows users to select the cut surface size depending on the workpiece.
It is used for drag soldering and pre-tinning of lead wires.
Type F, tinned surface only, is available for Shape BC/C. Try Type F when troubling with excessive solder amount or bridge to neighboring parts.
* Not suitable when heavy heat capacity is required.
Difference between BC/C type and BCF/CF type
Movie helps you to understand it easily.
| Shape BC | Shape C | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Difference | Shape | This type has a shape like a cone cut at a slant. | This type has a like a column cut at a slant. |
| Heat capacity of tip | In Shape BC with its conical shape, the nearer to the base, the thicker the diameter. Therefore, although these types have the same diameter Φ1, Shape BC has more heat capacity. | ||
| Commonality | How to select tip size | Please select the cut surface size depending on the workpiece. | |
| Others | In case of a chip condenser, we recommend soldering it with Shape BC or C to form ideal solder fillet, which can be hardly formed with Shape B or D. | ||
Soldering tiny chip parts such as 0603
 | Put the cut surface to the land. Some IC is specified by manufacturer not to be touched electrode by tip end. The other tip shapes are recommended. |
Soldering chip parts
 | Put the cut surface to the land and drag the tip slowly while feeding solder. Some IC is specified by manufacturer not to be touched electrode by tip end. |
Drag soldering
 | Put the cut surface to the leads and drag it slowly. Apply flux to leads and land pads before soldering. It prevents the troubles such as solder bridge. |
 | |
Pre-tinning lead wire
 | Put the cut surface to the lead and drag the tip slowly while feeding solder. |
Point soldering
 |
|
Melting and removing coil coatings
 |
|
| Weight | 0.00994 kg |
|---|


